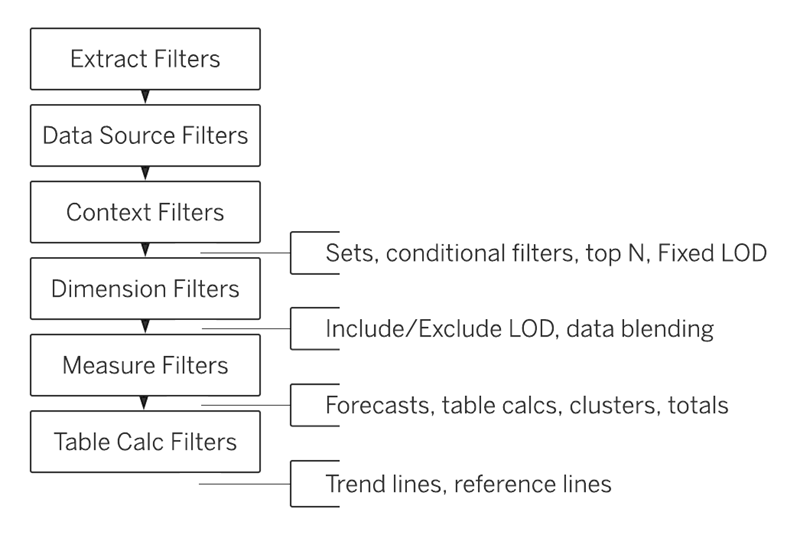
When building complex dashboards in Tableau, you'll work with many filters and table calculations. What many people don't realize—especially those new to Tableau—is that filters always run in a specific order called the "Order of Operations." This can lead to unexpected results when using multiple filters.
Context filters offer a way to change this default order, letting certain filters run first regardless of their normal position. To understand their benefits, let's look at how Tableau's Order of Operations works.
The Order of Operations: A Simple Example
Let's use a simple example with the Sample Superstore dataset to demonstrate how filters are influenced by the Order of Operations. We want to display the top 10 customers by sales in New York City, which requires two dimension filters:
- First, we apply a dimension filter for City: New York City
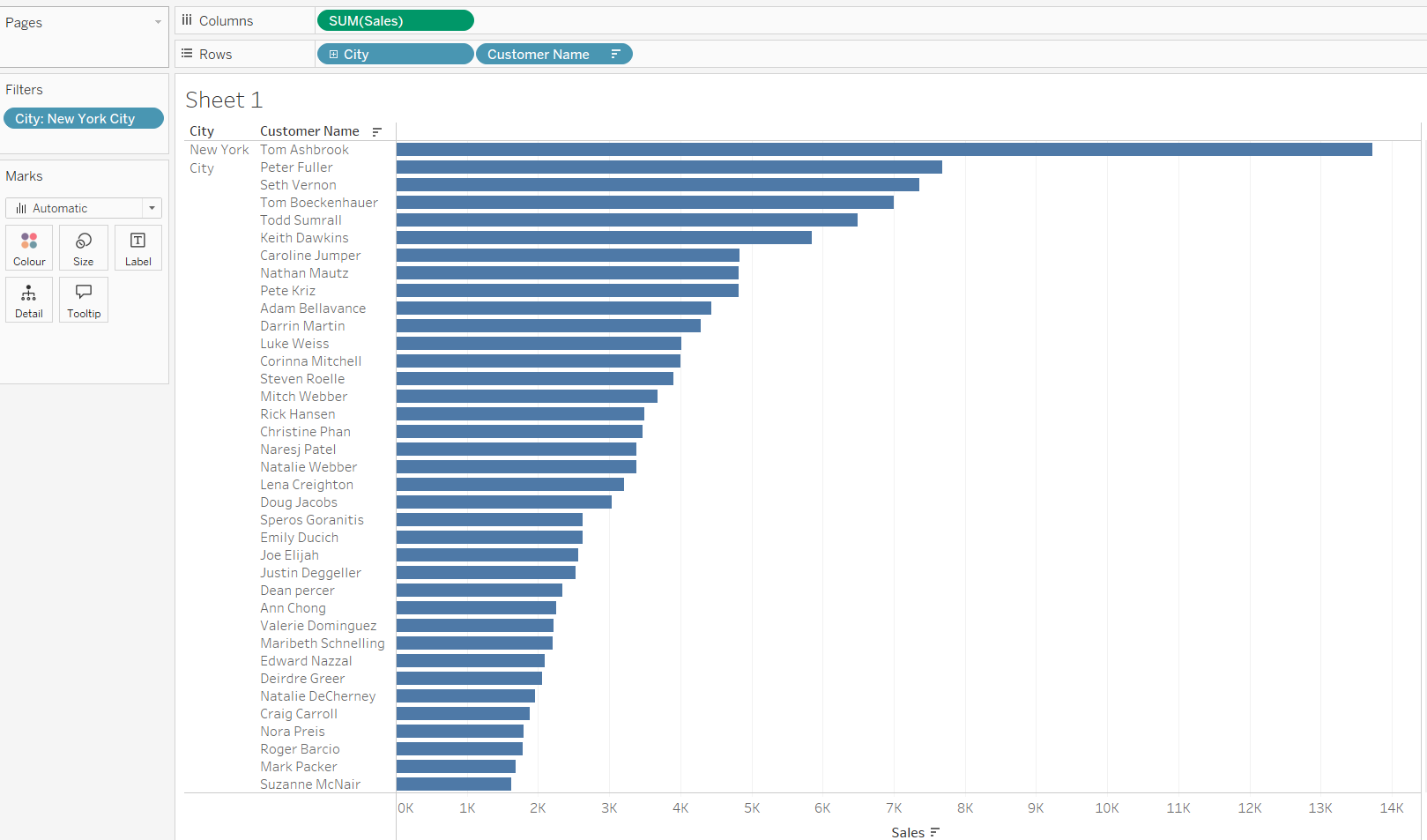
- Next, we set a Top N filter on Customer Name to show only the top 10 customers
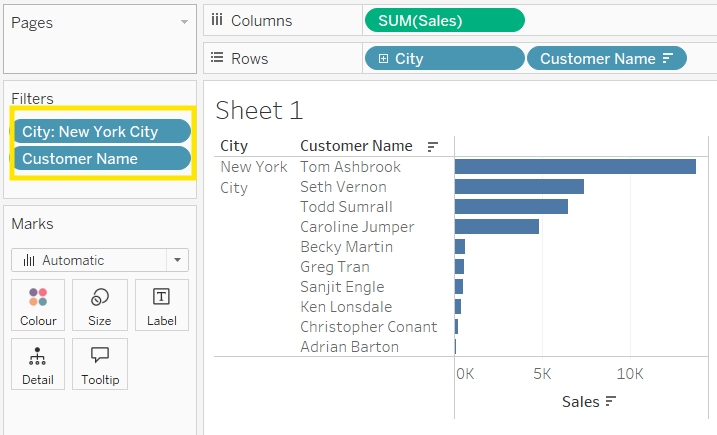
Looking at the results, we see 10 customers, but something's wrong. The names don't match with what we have seen before. Peter Fuller, who ranked second when using only the City filter, is now missing from our view.
What happened? Although we wanted to find the top 10 customers in New York City, we're actually seeing the overall top 10 customers instead.
The problem is how Tableau processes these filters. In the Order of Operations, Top N filters run before dimension filters. This means Tableau first finds the top 10 customers across the entire dataset, and only then filters for New York City. So we don't get the top 10 customers specifically from New York City.
How Context Filters Help
This is where context filters become useful. A context filter in Tableau acts as a foundation for other filters. It runs first (except for data source and extract filters) before other filters follow the standard order. This lets you control the Order of Operations and avoid filter conflicts.
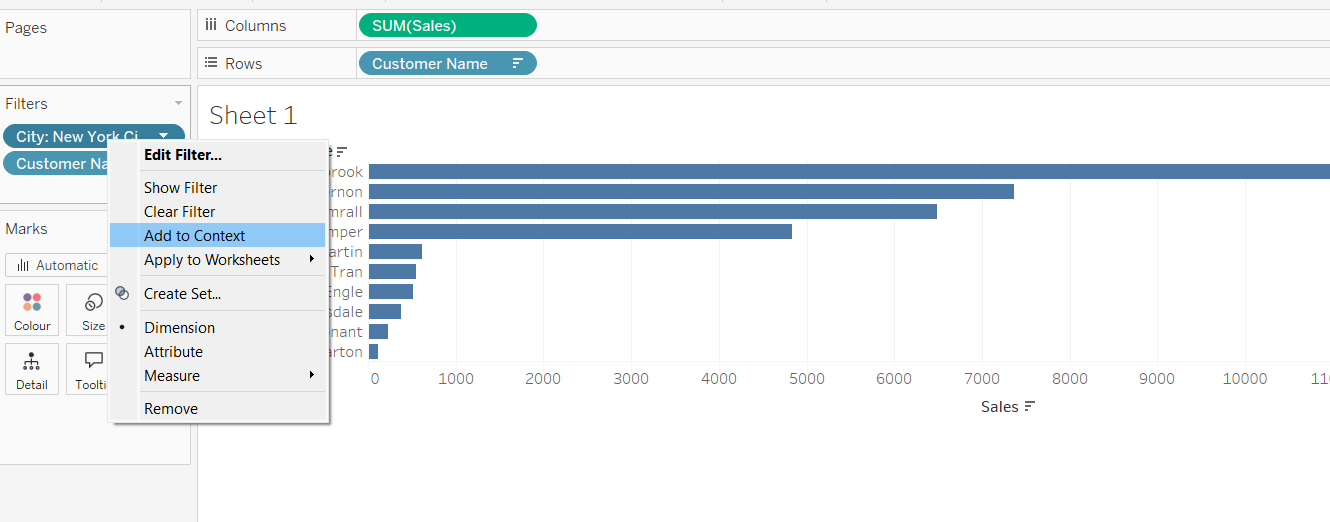
Adding a context filter is easy—just right-click on your filter, which will open the filter menu, and select "Add to Context." The context filter will show as a gray pill.
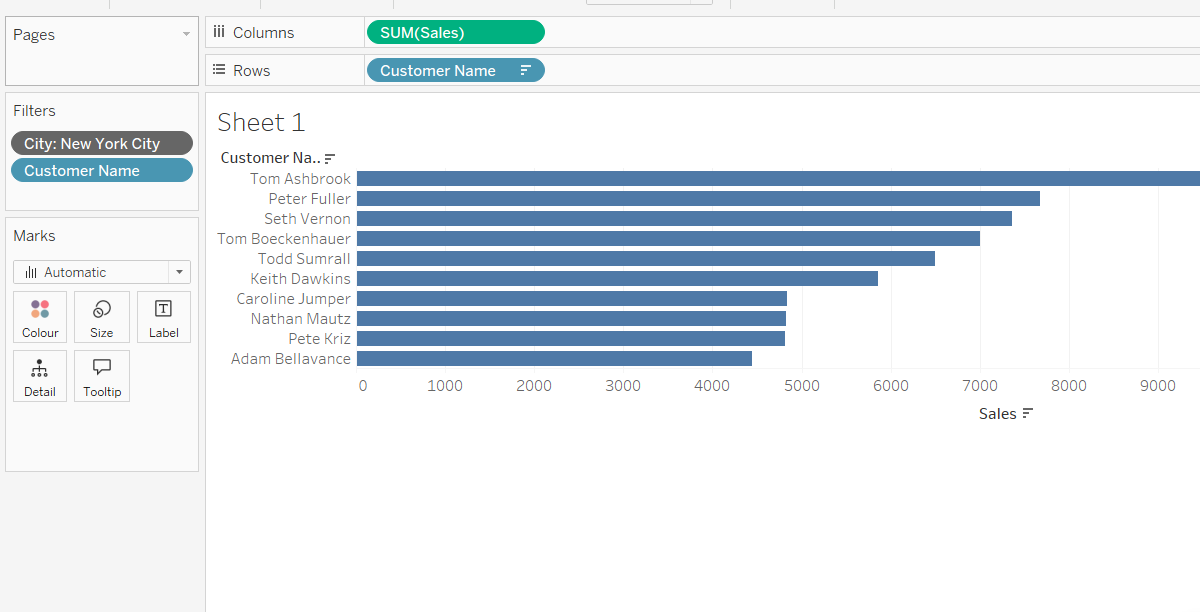
After making this change, you'll see the names in your Top 10 list have updated and now match the ranking you saw before adding the Top N filter. This confirms that Tableau first applied our context filter for New York City, and only then filtered for the top 10 customers.
