While preparing your data, it is very important to assign the appropriate data type. Alteryx supports different data types, such as string, numeric, date-time, boolean, as well as spatial objects.
Let's have a closer look at string and numeric options.
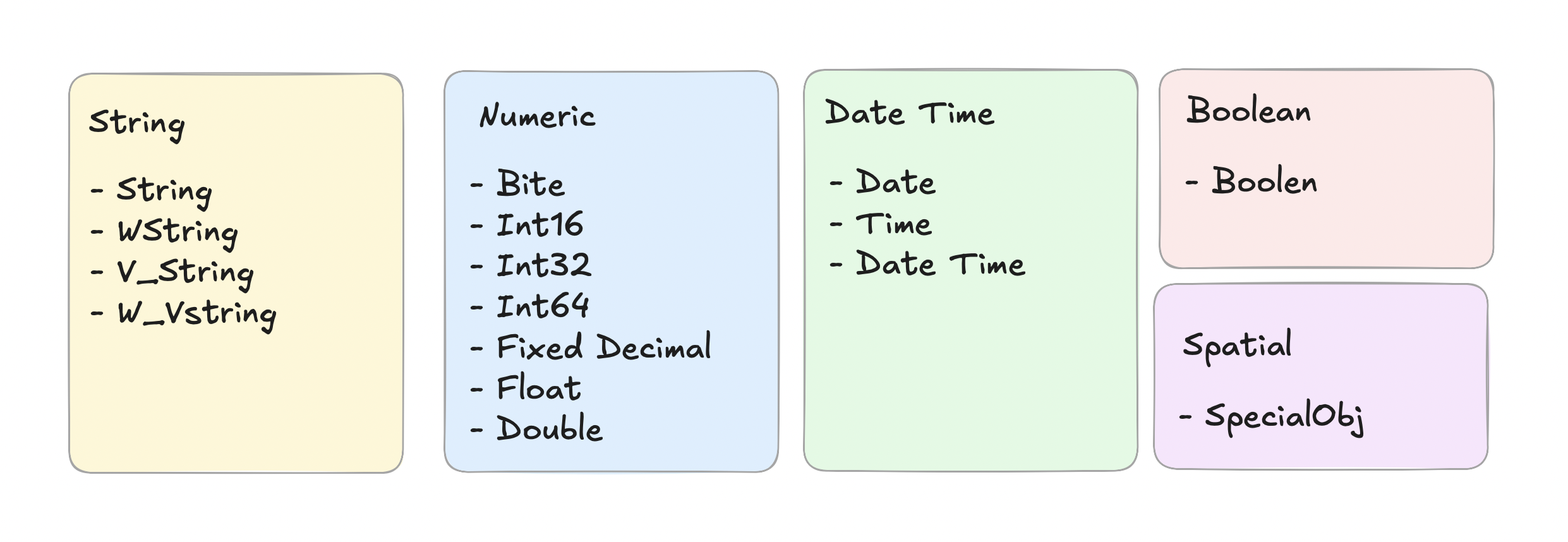
String (Text) Types
There are 4 options available:
- String – fixed length, accepts only Latin-1 characters. Use it when you are sure about the length and the type of characters. Benefit: workflow runs faster. Maximum 8192 characters.
- WString – like String, but accepts any character, including Unicode or international characters. Use it when you need non-Latin characters. Maximum 8192 characters.
- V_String – flexible length, automatically adjusts to the text length, but only accepts Latin-1 characters. Use it when you are not sure about the maximum length.
- V_WString – flexible length and accepts all characters. Use it when you need non-Latin characters and don’t know the length.
Numeric Types
- Byte – very small number, only positive whole numbers (0–255). Good for things like age.
- Int16 – small whole numbers (–32,768 to 32,767).
- Int32 – most normal whole numbers (–2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647).
- Int64 – huge whole numbers (–9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807). Good for things like world population.
- Fixed – exact decimal numbers, no rounding. Good for money, prices, or percentages.
- Double – very precise decimal numbers. Good for measurements, averages, or stats.
- Float – decimal numbers with slight rounding. Good for big datasets or approximate calculations. Faster for processing large amounts of data.
You can find more information on the Alteryx page: https://help.alteryx.com/current/en/designer/file-types-support/data-types.html##
