Filtering data is a useful step in refining information, allowing us to spotlight aspects of a dataset that are mostly relevant to the end user. In Tableau, data filtering extends to both dimensions and measures, introducing a dynamic interplay of options that adapt to the unique needs of analysis.
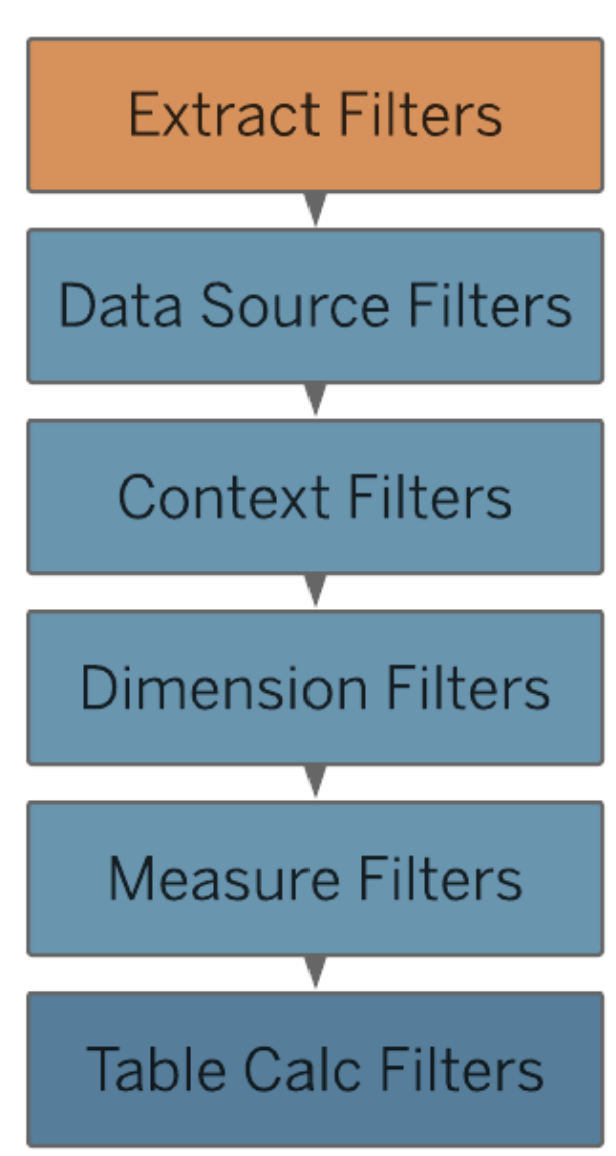
It is important when using filters to also keep in mind Tableaus Order of Operations so have a brief look at the image below:
You are able to filter to specific fields by clicking and dragging the field from the data pane into the Filters Box. When this is done for a Dimension, a pop up will show:
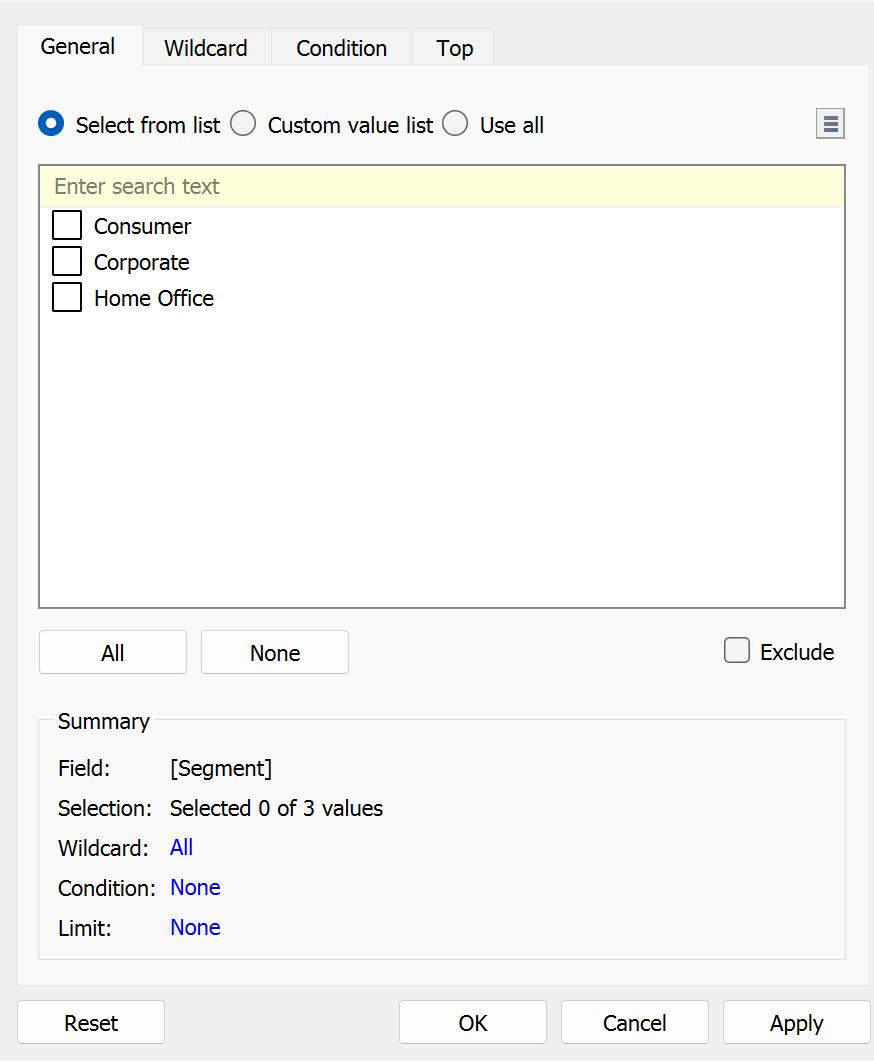
There are 4 options to be able to filter by.
- General: Select members of the dimensions that you would like to just include or exclude by manually selecting.
- Wildcard: Set up a wildcard rule which searches for data points that 'starts with', 'end's with', 'contains' or 'exactly matches'.
- Condition: Filter values based on specific conditions using a Field measurement or using a formula. (Parameters can be used here)
- Top: Filter by the top or bottom N fields when N is specified. Similarly this can be done using a field or formula and therefor a parameter can be used to.
When filtering a Measure a different pop up window will show up:
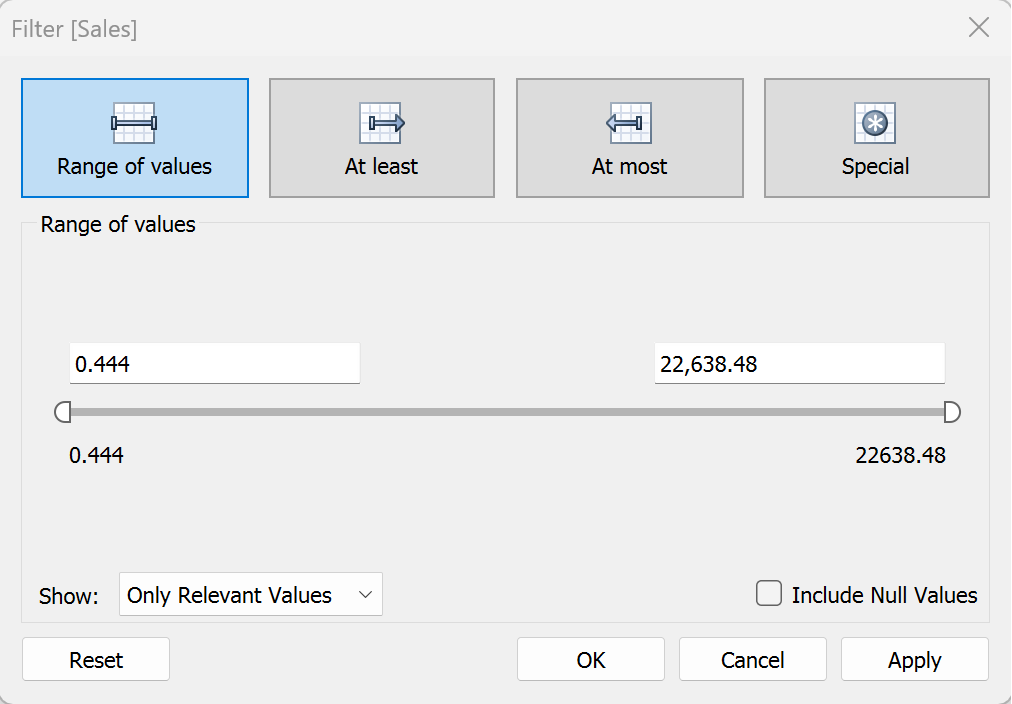
- Range of Values: Include all values within the specified range
- At Least: Include all values above a specified value
- At Most: Include all values below a specific value
- Special: Set filter specifically for null or non-null values
So keep in mind the order of operations and enjoy using filters!
