A Key Performance Indicator (KPI) without context is just a number. To make a KPI useful, you can provide a relevant comparison. One of the most common and powerful forms of context is a Year-Over-Year (YoY) comparison, which gauges performance by measuring the current month's profit against the same month in the prior year.
This approach provides a clear benchmark that can account for seasonality and long-term trends. Below is a detailed, two-step process to build this calculation using common functions found in Tableau.

Step 1: Create current month profit calculation
To isolate the profit for the current month, you must create a date boundary using logical conditions. This calculation effectively flags only those profit records that fall within the current calendar month.
The goal is to check if the Order Date is greater than or equal to the start of the current month, AND strictly less than the start of the next month.
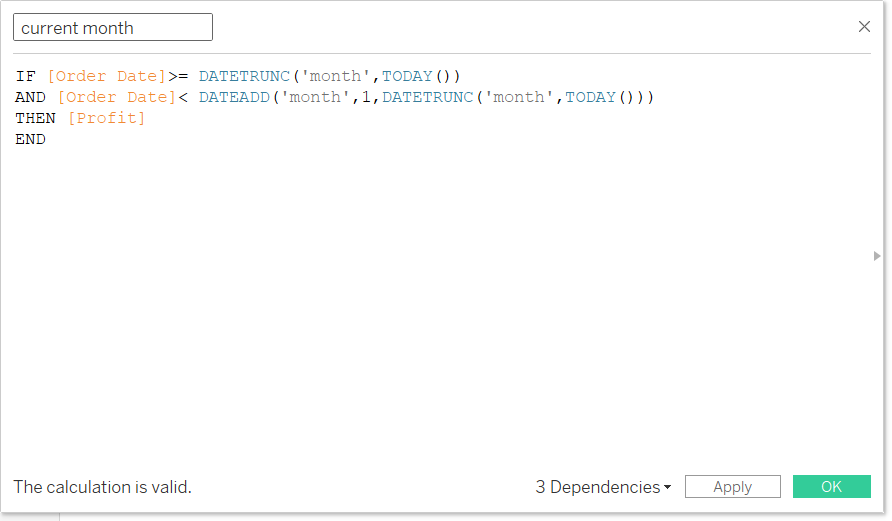
IF
[Order Date] >= DATETRUNC('month', TODAY())
AND
[Order Date] < DATEADD('month', 1, DATETRUNC('month', TODAY()))
THEN [Profit]
END
Function Breakdown:
DATETRUNC('month', TODAY()): This returns the first day of the current month (e.g., if today is 23/08/2025, it returns 01/08/2025). This sets the lower date boundary.DATEADD('month', 1, DATETRUNC('month', TODAY())): This returns the first day of the next month (e.g., 01/09/2025). Using a "less than" comparison with this date ensures all days of the current month are included without having to worry about months having 30 or 31 days.
Step 2: Create a same month previous year calculation
The next step is to calculate the profit for the same calendar period, but shifted back by exactly one year. This uses a very similar structure to Step 1, with a slight modification using the DATEADD function to shift the entire range.
The date boundaries are calculated by taking the Current Month boundaries and shifting them back by one year ('year', -1).
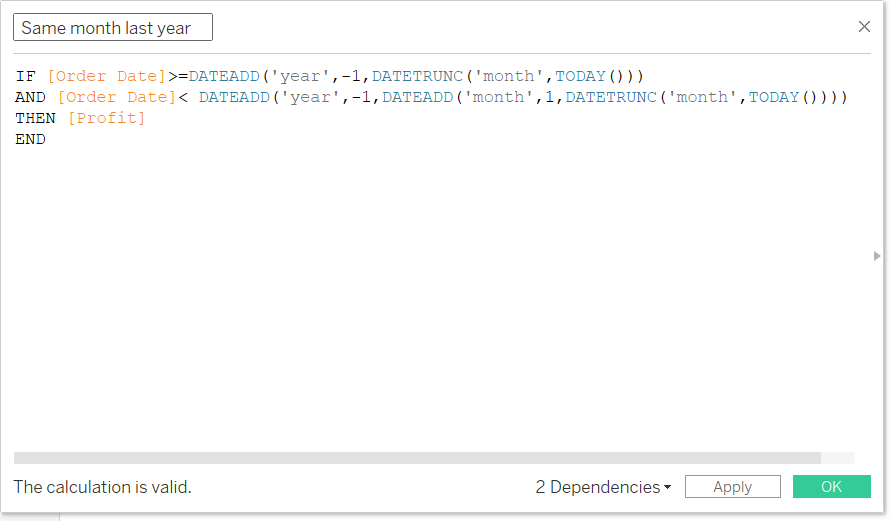
IF
[Order Date] >= DATEADD('year', -1, DATETRUNC('month', TODAY()))
AND
[Order Date] < DATEADD('year', -1, DATEADD('month', 1, DATETRUNC('month', TODAY())))
THEN [Profit]
END
Function Breakdown:
DATEADD('year', -1, ...): This function is wrapped around the date boundaries calculated in Step 1. It reliably subtracts exactly one year, ensuring the comparison is precisely the same month from the previous year (e.g., shifting the range 01/08/2025 to 01/08/2024).
Step 3: Format as desired
The final step is simply to format the visualisation and add any further context such as YoY percentage change using the values created.
