When is a table not a table?Snowflake has three main types of tables in order to accommodate various data storage needs: permanent, transient, and temporary tables. Each table type has different traits that cater to different scenarios. In this blog, we will attempt to summarise each of them and give some scenarios.
Permanent Tables
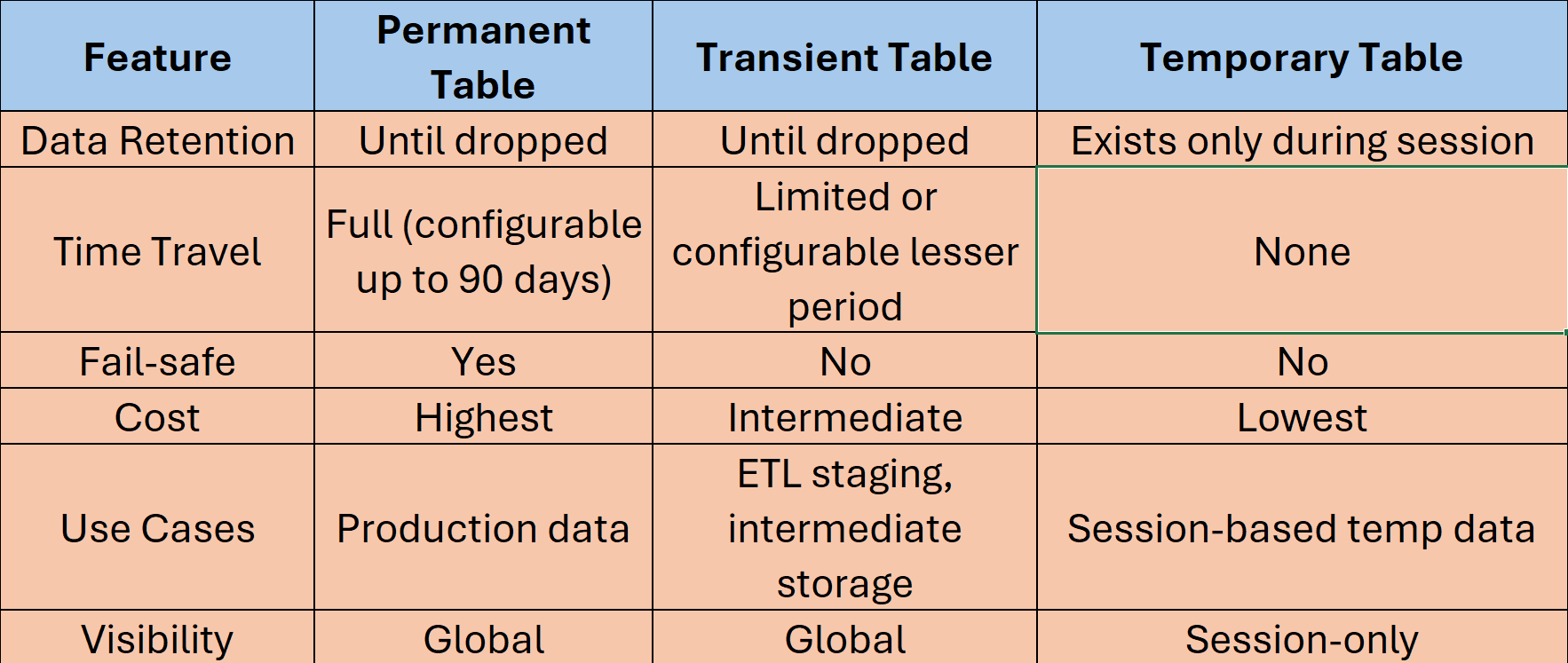
Permanent tables are Snowflake’s default tables. Permanent tables are kept until they are deleted or dropped by a user. Permanent tables also include Snowflake’s powerful data protection, which is comprised of Time Travel and Fail-Safe.Time Travel allows you to restore data from any point within a configurable retention period (up to 90 days, depending on which version of snowflake ).Because of their longevity and safety features, permanent tables are the default for most use cases; however, they are obviously also the least cost efficient and, if used too liberally, can lead to a large Snowflake bill.
Temporary Tables
Temporary tables exist for the duration of a user session and are dropped once the session ends or the connection is closed. They are not visible or accessible outside the session. They have very limited time-travel and no fail safe. This makes them unsuitable long long-term needs.However, it is good if you need you to quickly acsess somthing for short-lived scratch data, intermediate calculations, or transient data.Temporary tables are good in scenarios like data transformation during a session, or incremental steps of a pipeline that you are working on if you don't want to have to rerun all the tables over and over due to time or cost considerations.
Transient Tables
Transient tables are a middle ground between permanent and temporary tables. Like permanent tables, data in transient tables remains until dropped by a user. The main difference is that transient tables have no Fail-safe period, whilst Time Travel retention is limited, thereby reducing storage costs.The reduction of fail-safe and time travel measures means that there is less overhead in managing and storing data snapshots, making transient tables a practical choice for use cases where data can be regenerated/is less critical. Such as intermediate steps in ETL pipelines. This balance enables an organisation to optimise its Snowflake storage costs while keeping data available for a reasonable time window.
Comparison Table of Snowflake Table Types