What is a semantic model?
The semantic model describes the dataset and what is inclusive within it. It allows users to ask questions across multiple data objects, to ultimately see trends across time over unrelated data columns, by relating them through relationships, to get a more holistic view of how the business is performing for example.
It keeps only the columns that are relevant and assigns them human readable names for easy reference. Ultimately it is a translation layer from data engineering into data analysis and application.
The below image is an example of what the semantic model may look like
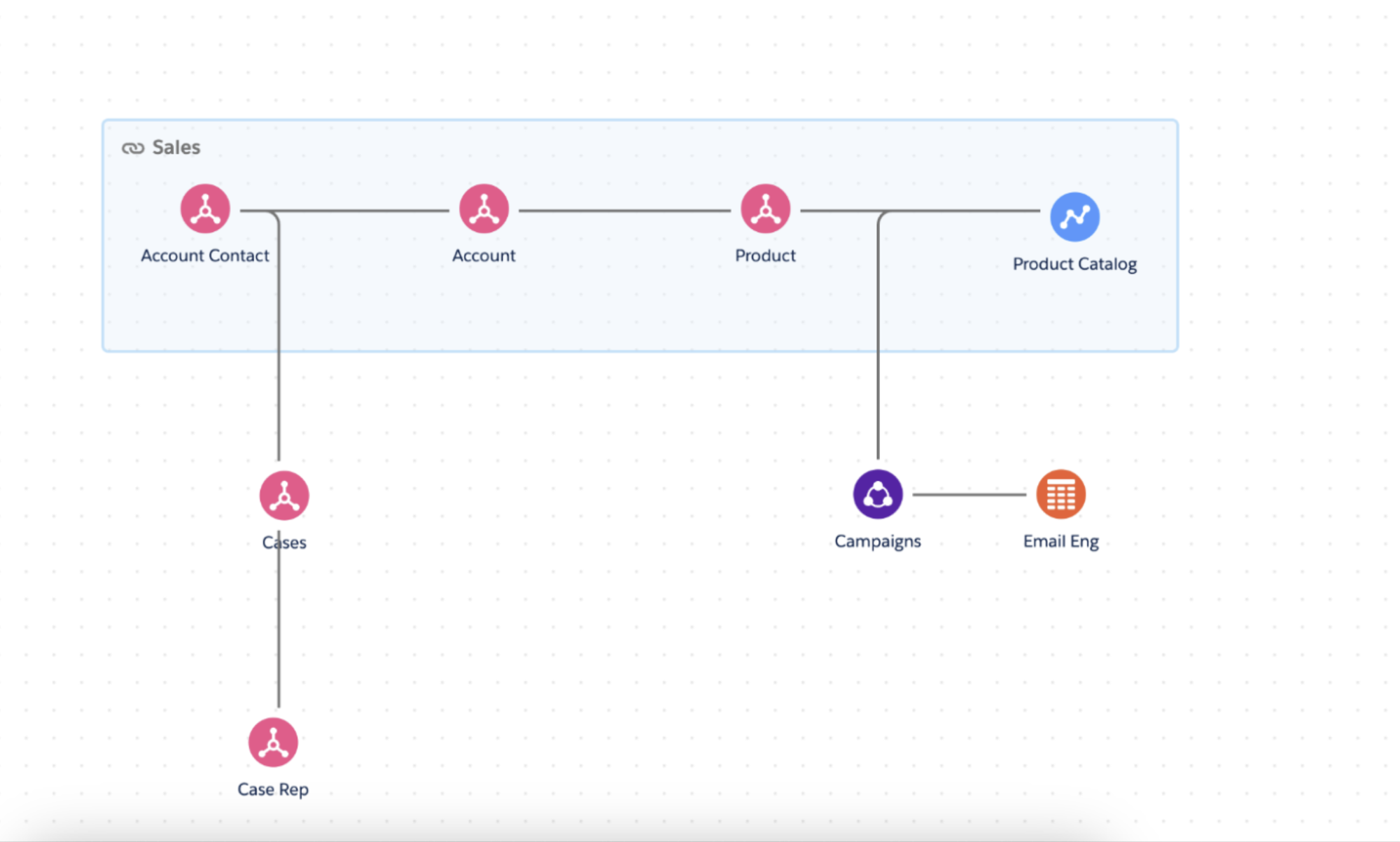
Why use a semantic model?
It is a way to flexibly link together two or more unrelated tables in order to get a holistic view across many areas/aspects of a business enabling the user to create calculated dimensions and measures, enabling you to create metrics and many more. They are also essential for Agentforce AI to be able to work.
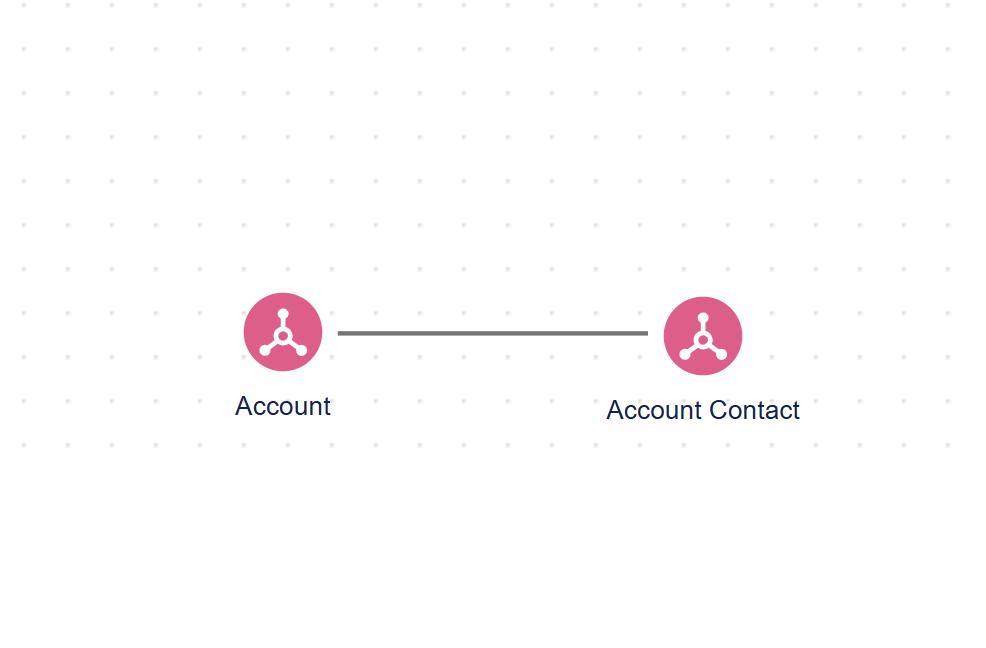
How to create a semantic model?
There are two ways to create a semantic model, either from scratch or based on an existing model.
To create from scratch
In workspace via the home page, you can use the add dropdown on the top right hand corner to create a new semantic model.
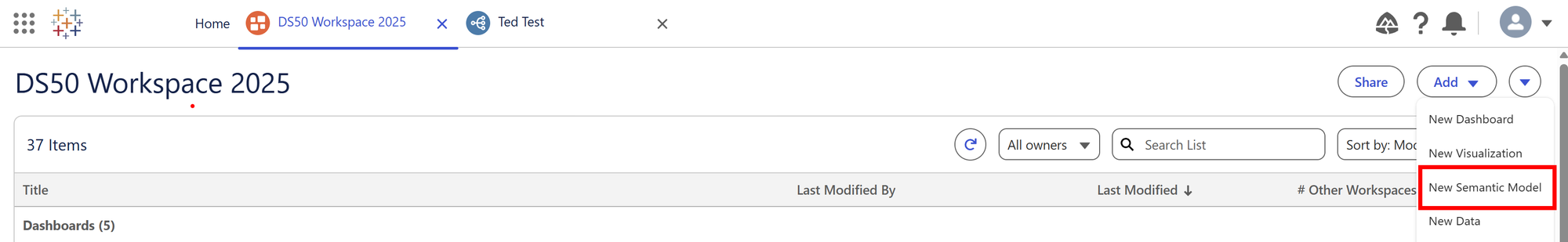
Here you will be given the option to choose from a variety of data objects, such as data lake objects or data model objects, depending on what data you have uploaded into the data streams tab in Data cloud.
You can then select which data objects you want to add;
DLO’s (data lake objects) are raw, unfiltered data, typically large tables from which you are wanting to extract data and insights from.
- For example - 'Orders'
DMO’s (data model objects) are polished versions of DLOs, which have been cleaned and edited suitably for the users intended outcome.
- For example could contain - OrderID, Customer Name, Price, Discount etc
To add a relationship, you can either flick the toggle to let Einstein create its suggested relationships, or you can do it manually.
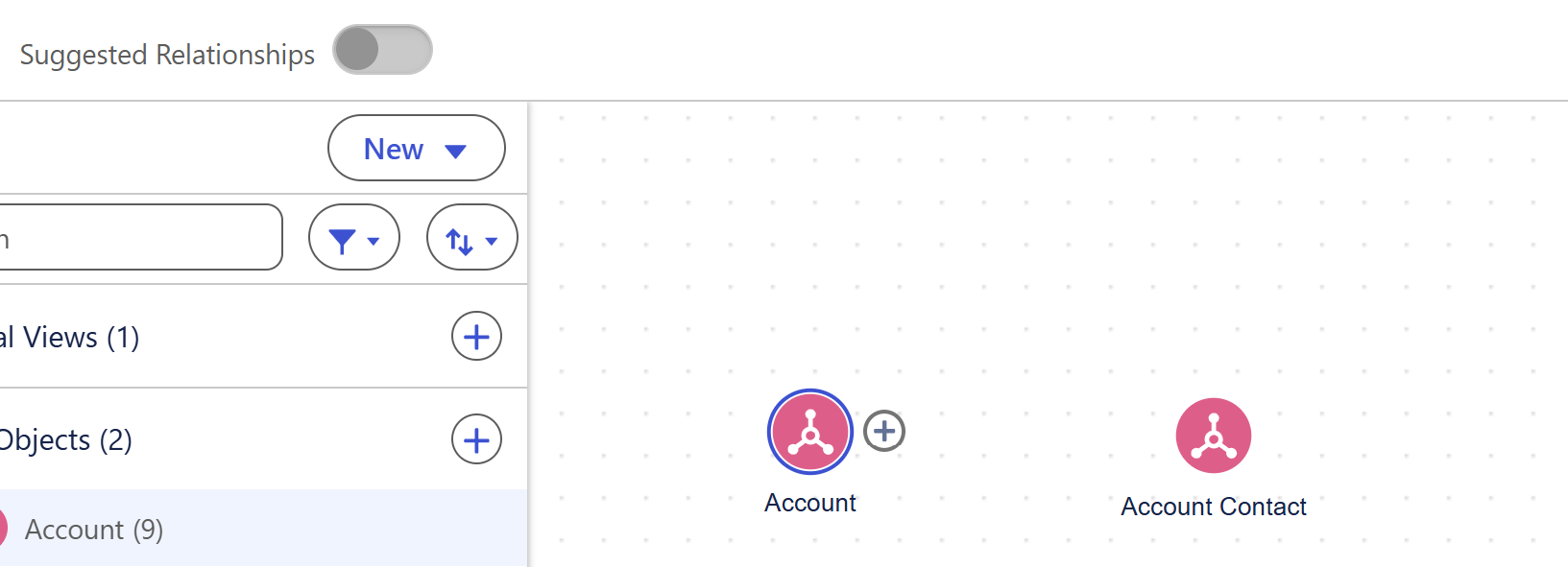
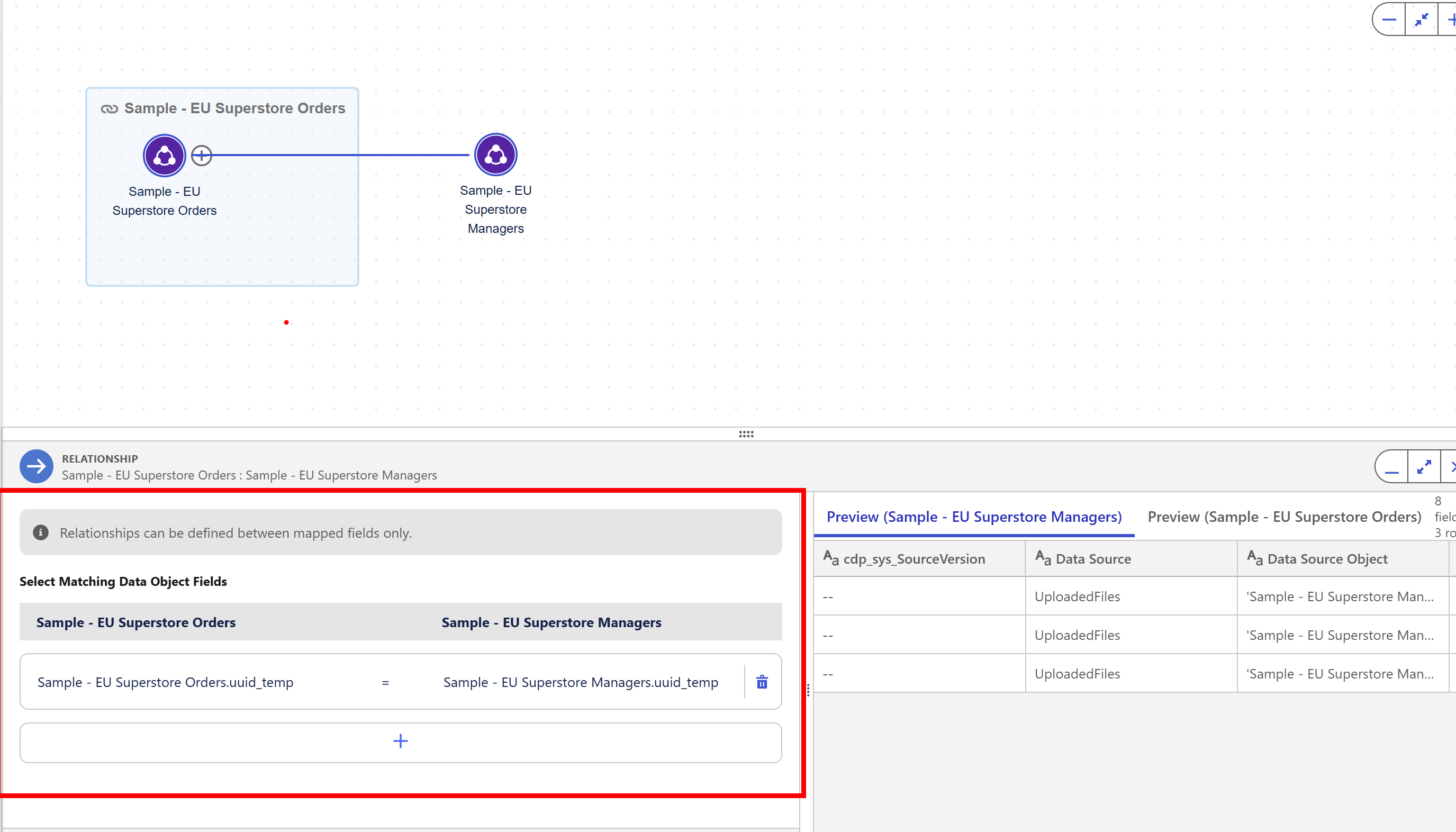
To do it manually, you can click the plus button next to one of the Data objects you have dragged into the view and then can select from the dropdown where you want to create the relationship between.
You can then come down to the relationship tab at the bottom of the screen and select two common fields to ‘match data object fields’, similar to how you would with the noodles in relationships in Tableau desktop in the data source pane. Be sure to click the add button at the bottom, to lock it in. Example below:
Create based on an existing model
You can create a semantic model based on an existing model, by adding data objects and semantic definitions. This is useful because the new model will stay connected to the original model, but if you make changes to the original model, these will only be pushed to the new, extended model.
Think of it like making a copy of a sheet, keeping all the work done on sheet A but any updates added to sheet B won’t affect sheet A.
This can be done in the semantic model part of the data cloud menu. By clicking the new model button in the top right hand corner, you are given the option to create from an existing model.
Once you click next, you will be presented with the opportunity to choose a current semantic model. By clicking the button on the left hand side, you can choose which semantic model you want to extend.
You can then choose a new semantic model name and API name and give it a description. Then you can use the same process as mentioned above for creating relationships between different data lake objects (DLOs) or data model objects (DMOs).
See below for an example of selecting a matching data object field:
Hope this helped.
