What is a Logical View?
A logical view is a data object that’s made up of many tables that are connected to each other using transformation join types. You can create a logical view in Tableau Semantics to connect data objects. You can then query the enriched dataset like a regular data object without understanding the underlying objects. The logical view is a separate object in the semantic model and has its own fields. The logical view can be used in relationships, calculated fields, metrics, and any other semantic definition.
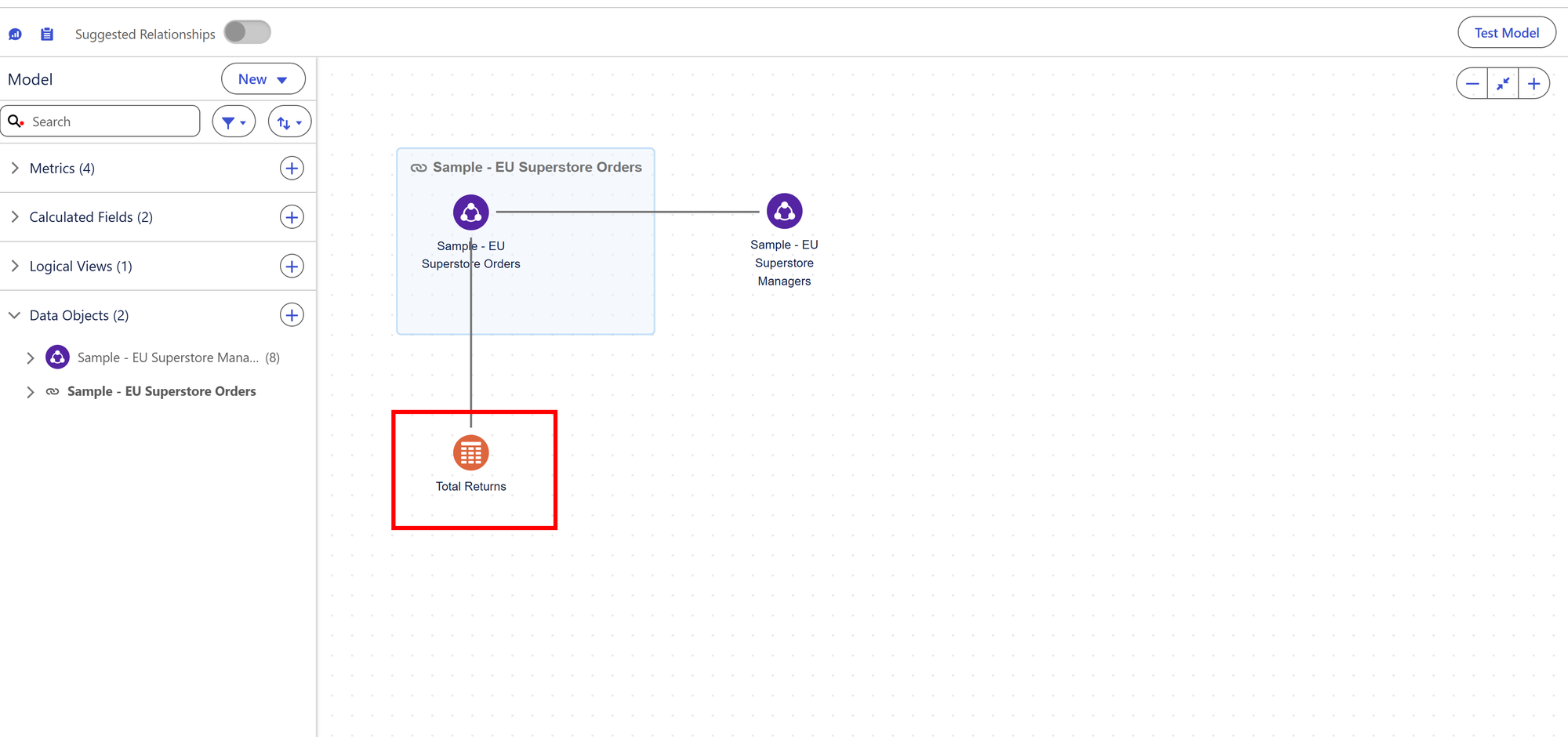
You are able to union and/or join multiple data objects in almost a separate 'bubble' to create one larger data object, which can then be taken back into the semantic model where you can then create relationships between your new logical view and other data model objects.
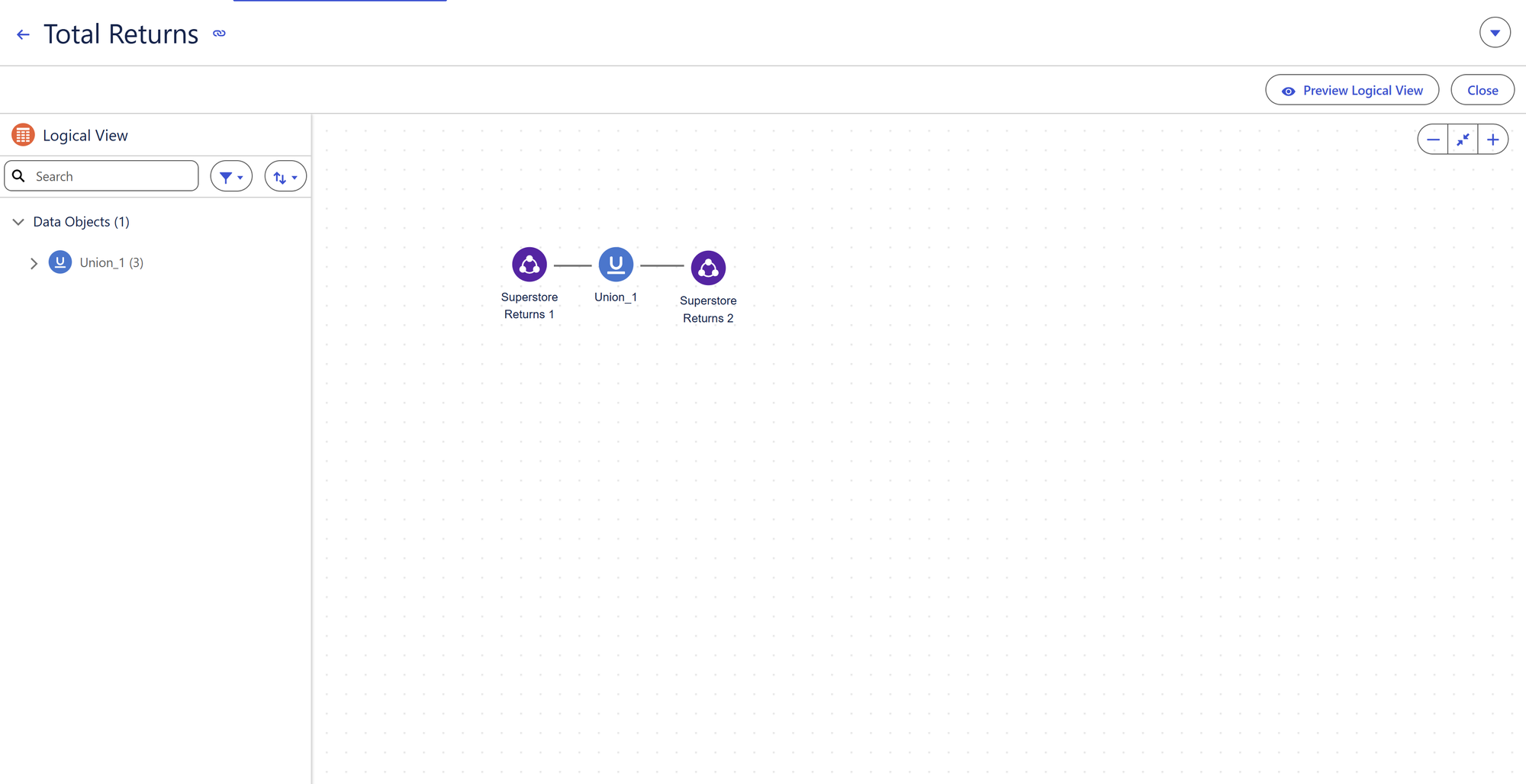
Why use a Logical View?
A good example would be if you had 12 single months of sales clothing data objects and wanted to see which items of clothing were selling the most and at what times of year etc. You could bring these 12 individual data objects into a logical view and then union all together so that they all stack on top of each other. This would create a logical view where you could then relate this logical view to a data model object containing data on how much each item of clothing costs to make, back in the semantic model in order to go on to visualise how much profit you were making etc.
