DAX stands for Data Analysis EXpressions. We use this in Power BI Desktop rather than the Power Query Editor to most commonly create:
• Calculated columns - A column that lives inside of the table, which is calculated at the row level. An example is below, calculating the revenue per row.
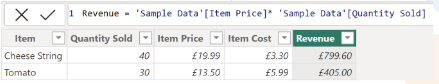
• Measures - Something used in your visualisation. An example below, creating a measure for the total number of transactions within a table. It essentially counts the number of rows in the table, where one row represents a transaction. Measures must be aggregated so cannot be performed at a row level.
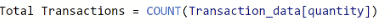
Similarly to Tableau's Table Calculations and Calculated Fields, there are different types of DAX functions, which can be explored further by clicking the links below:
